Title: “Cloud Security Solutions Comparison: AWS vs Azure vs GCP (2025 Official Guide)”
Introduction
Securing workloads in the cloud is no longer optional — it’s essential. When you use AWS, Azure, or GCP, their built-in security tools and architectures differ significantly. This guide compares cloud security solutions from AWS, Azure, and GCP using official, confirmed sources. Through this, you can better choose the cloud security stack that fits your organization’s needs and operational maturity.
Shared Responsibility & Security Foundations
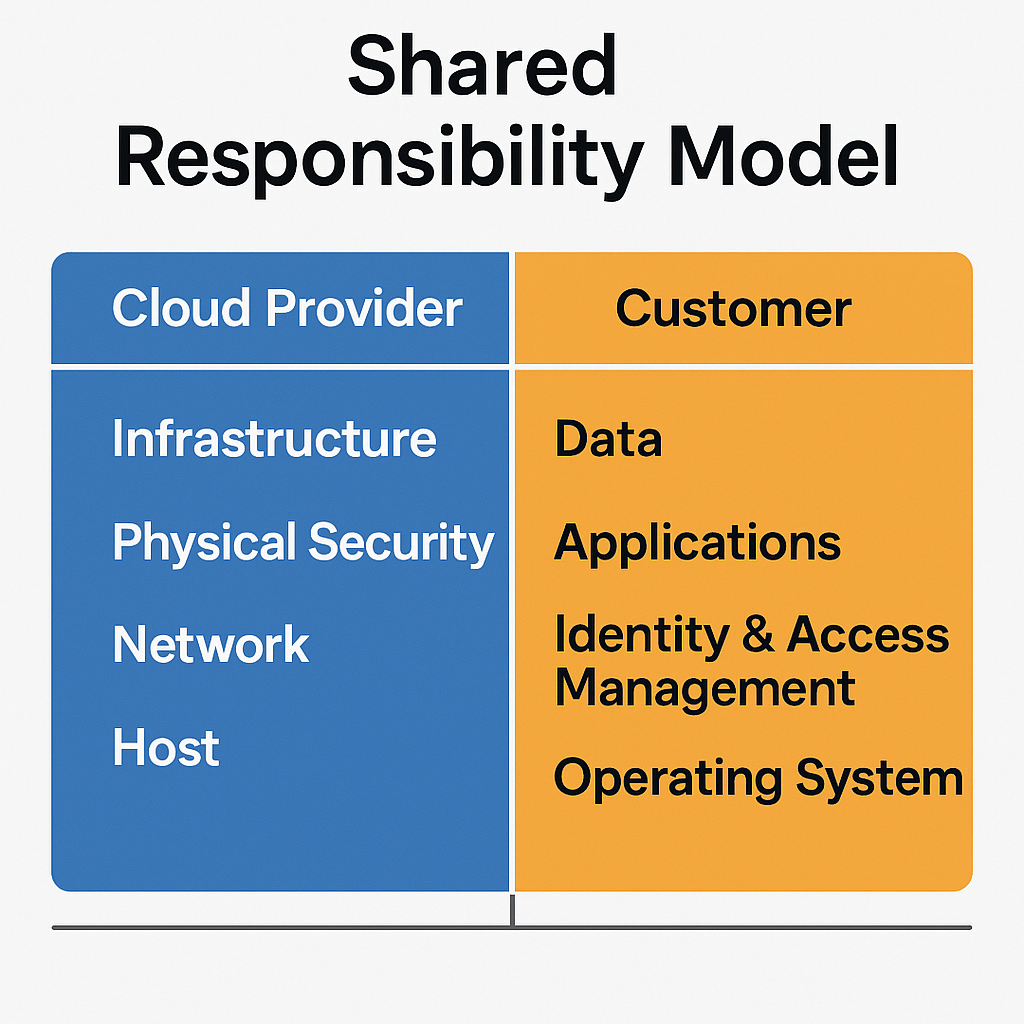
All major cloud platforms adopt a Shared Responsibility Model:
The cloud provider secures the underlying infrastructure (data centers, network, hypervisors).
The customer is responsible for securing what runs inside the cloud (identity, applications, data, configurations).
On top of that model, every robust cloud security strategy should address:
Identity & Access Management (IAM) with least privilege
Network segmentation, firewalls, micro-segmentation
Encryption in transit and at rest
Logging, monitoring, and threat detection
Security posture management and automatic drift detection
Misconfiguration detection and remediation
These principles form the baseline; below, we compare how AWS, Azure, and GCP implement them differently.
AWS Cloud Security
Key Official Services & Features
AWS provides a broad security portfolio including IAM, GuardDuty, Detective, Macie, Security Hub, CloudTrail, Config, KMS, Shield, WAF, CloudHSM, etc.
Amazon Web Services, Inc.
+3
AWS Documentation
+3
Amazon Web Services, Inc.
+3
GuardDuty is AWS’s managed threat detection service analyzing API calls, VPC flow logs, DNS logs.
AWS Documentation
+1
Security Hub aggregates security findings across services (GuardDuty, Inspector, etc.).
AWS Documentation
+1
Detective helps with root-cause investigations by linking events and logs.
AWS Documentation
AWS KMS and CloudHSM support key management and HSM-based keys.
AWS Documentation
+1
Shield & WAF protect against DDoS and common web attacks.
AWS Documentation
+1
Strengths
Very mature, feature-rich security ecosystem
Strong compliance portfolio (AWS handles compliance for many infrastructure components)
AWS Documentation
+1
Extensive third-party vendor integrations
Fine-grained IAM and encryption controls
Considerations
High complexity—many services to configure correctly
Risk of misconfiguration by users
Costs can grow if many advanced security tools are enabled
Azure Cloud Security
Key Official Services & Features
Microsoft positions Azure with built-in security controls, defense-in-depth, threat detection.
Microsoft Azure
+2
Microsoft Azure
+2
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a unified security posture and threat protection solution (CSPM + CWPP).
Microsoft Learn
+1
Azure also supports Azure Policy, Blueprints, and the Microsoft Cloud Security Benchmark (successor to Azure Security Benchmark) for standardizing security posture.
Microsoft Learn
+1
Identity control is via Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD), with conditional access, MFA, RBAC.
Microsoft Azure
+1
Network protection: Azure Firewall, Network Security Groups, Application Gateway WAF.
Microsoft Azure
Key Vault is used for secrets, keys, certificates, with HSM support.
Microsoft Azure
+1
Strengths
Deep integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem (Windows, AD, Office 365, etc.)
Policy-driven governance across subscriptions using Azure Policy & Blueprints
Good support for hybrid (on-premises + cloud) environments
Considerations
Licensing and complexity in combining Defender, Sentinel, etc.
Requires governance discipline to avoid policy conflicts
GCP Cloud Security
Key Official Services & Features
Google’s Security Command Center (SCC) provides unified security posture management and threat detection in GCP.
Google Cloud
GCP provides encryption at rest and in transit by default; supports Cloud KMS, external key managers (EKM), and hardware security modules.
Google Cloud
VPC Service Controls enable creating strong perimeters around services to reduce data exfiltration risk.
Audit Logging, Cloud DLP, and other data protection tools are standard parts of GCP’s security offerings.
Google Cloud
Strengths
Strong default encryption and key management
Built-in mechanisms to limit cross-service data exposure (VPC Service Controls)
Simple model in many respects compared to AWS (fewer overlapping services)
Considerations
Some advanced features may lag in maturity compared to AWS or Azure
Need to carefully design organization-wide policy scaling
Illustration Placeholders
Conclusion
When comparing cloud security across AWS, Azure, and GCP, each platform brings strengths and trade-offs. AWS offers the broadest and most mature security ecosystem. Azure excels when you already operate in Microsoft environments and want governance automation. GCP emphasizes secure defaults, streamlined models, and strong data protection controls.
Your choice should depend on your organization’s existing infrastructure, compliance requirements, team capability, and how much governance and automation you want. Regardless of the cloud, ensure you follow the core principles (least privilege, encryption, monitoring, posture management) and avoid misconfiguration risks.
References / Authoritative Sources
AWS, “Security, identity, and compliance services”, AWS official documentation.
AWS Documentation
+2
Amazon Web Services, Inc.
+2
AWS, “Security and compliance overview”, AWS Whitepaper.
AWS Documentation
Azure, “Azure Cloud Security”, Microsoft official page.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft, “Microsoft Defender for Cloud – introduction”, Microsoft Docs (2025).
Microsoft Learn
Microsoft, “Microsoft cloud security benchmark (v1)”, Microsoft Docs (2025).
Microsoft Learn
Google Cloud, “Security Command Center”, Google Cloud official page.
Google Cloud
If you like, I can deliver this as ready-to-paste WordPress HTML (with alt tags, heading structure, SEO meta) plus suggestions for actual image sources. Would you like me to do that?